by Götz-Andreas Kemmner
Successful restructuring projects require a high degree of behavioral change among the employees concerned. In order to bring about this change, business simulations can be a useful tool, as this case study shows.
An industrial company needed to restructure its production planning and control. The aim was to improve delivery readiness, reduce inventories and shorten throughput times. At the start of the project, a logistics business simulation was used to run through various alternatives in the process flows and to analyze and evaluate the results. In addition, the company management wanted to create an awareness and openness for the urgent need to make changes to processes right from the start of the project.
In round one, the game plan is based on the process that can be found in companies today: There are bottlenecks in production because the production areas are not coordinated with each other in terms of capacity. Quality problems also occur. At the end of the round, no customer receives their goods at the desired time.
In the next round, the capacities between the production areas are equalized. The introduction of in-process quality control is also on the agenda. Because customers require deliveries at fixed intervals, production orders are scheduled according to this rhythm. The analysis of the second round already shows the first improvements. This allowed production output to be increased by 63% and production quality to be improved by 43%.
Although production orders are now loaded into the system in line with market demand, only a delivery readiness level of 20% is achieved. In addition, inventories are only slightly lower and lead times are still unacceptable. The discussion continues on Why does one employee manufacture the entire product? Can’t production areas be merged? Why do stocks build up in front of the workstations even though the work content is balanced and the deliveries from external suppliers are coordinated with the order workload?
These and additional measures will be implemented and tested in the third and subsequent rounds. The key figures were gradually improved until almost all targets were achieved in the last round: delivery reliability 97%, production quality 88% (still quite sufficient), inventory reduction 54%, throughput time reduction per product from 13.6 to 2.9 minutes (-78%).
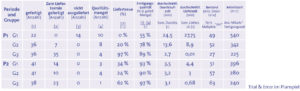
The results (table) show that the simulation game was successful. But business games can also be useful as an aid to change processes. The management consultancy Abels & Kemmner is currently developing a business game in cooperation with the Cologne University of Applied Sciences and the Institute for Production Technology and Organization (IPO) at the Cologne University of Applied Sciences, which will be carried out in a “production company for action-oriented learning”.
The benefits in a specific project
The participants experienced the connections and effects of their own decisions quickly and memorably in a playful way. They had a different responsibility in each new game round. The understanding of the problems of the other company divisions was thus experienced within just one round of the game. The environment of the business simulation game playfully “forced” the employees to think holistically. Furthermore, aspects such as the selection, implementation and evaluation of improvement measures, the analysis of improvement potential of individual measures and the transfer of knowledge were addressed and improved through this workshop.
A lot depends on his personality
The successful use of a business game is subject to many factors. However, the key to success is clearly in the hands of the game master. An experienced leader will always achieve performance-motivating learning success.
The situation where a participant informs the game master that they were against the group decision is a familiar one. It generally occurs This occurs when one or more planned game runs are unsuccessful. In the real business situation, problems often only come to light slowly, whereas in the world of business simulations this usually happens very quickly. One wrong decision can already lead to conflict, hidden or open.
In such situations, the game master is called upon. He must be able to lead participants back into the group and deal with dominant participants who need to make a name for themselves. This requires a good dose of empathy and the ability to overcome conflict situations by motivating the participants.
Furthermore, the simulation leader must have a reliable command of the business simulation’s numerical framework and be a proven expert in the areas of production organization and logistics. The players must be able to quickly understand and easily learn business interrelationships and interdependencies and also make their decisions on the basis of sound business data.
In addition to the difficult selection of a suitable business game for a company’s specific situation, the implementation of the game and thus the game leader is crucial for the start of successful project management of operational restructuring measures.
Business simulations can be a useful tool for imparting knowledge and changing employee behavior – especially in the case of upcoming restructuring projects, such a tool can be the basis for successful project management and provide helpful services during the implementation phase. This lays the foundation for sustainable and successful change. However, it must be emphasized that the actual work of restructuring lies in the detailed design and implementation of the concepts developed. The management game can “only” be an auxiliary tool, albeit an efficient one, for successful project management. A change in the way employees think and act can generally be achieved. faster, more cost-effectively and more sustainably by gaining your own experience. However, everyday business life is not suitable for this. The costs for wrong decisions, the time required and the duration to achieve results would be many times higher than simulating different situations in a “model world” of a business simulation. As a kick-off event and for project support, business simulation games are therefore a useful tool for achieving motivation, willingness to change and an understanding of the interrelationships and interdependencies of process changes among employees.

